4.7. 图算法范例
提示
范例源代码下载地址: PathFindingExamplesTest.java计算正连个节点之间的最短路径(最少数目的关系):
使用 迪科斯彻(Dijkstra) 算法解决有向图中任意两个顶点之间的最短路径问题。
使用 A* 算法是解决静态路网中求解最短路最有效的方法。
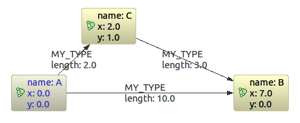
这儿是我们的范例图: